Here you can find Solar Panels and technological accessories related to Solar Energy: Click Here If you want to learn about Solar...
Here you can find Solar Panels and technological accessories related to Solar Energy: Click Here
If you want to learn about Solar Panels, to advise you before buying or to build your own Solar Panel: Click Here
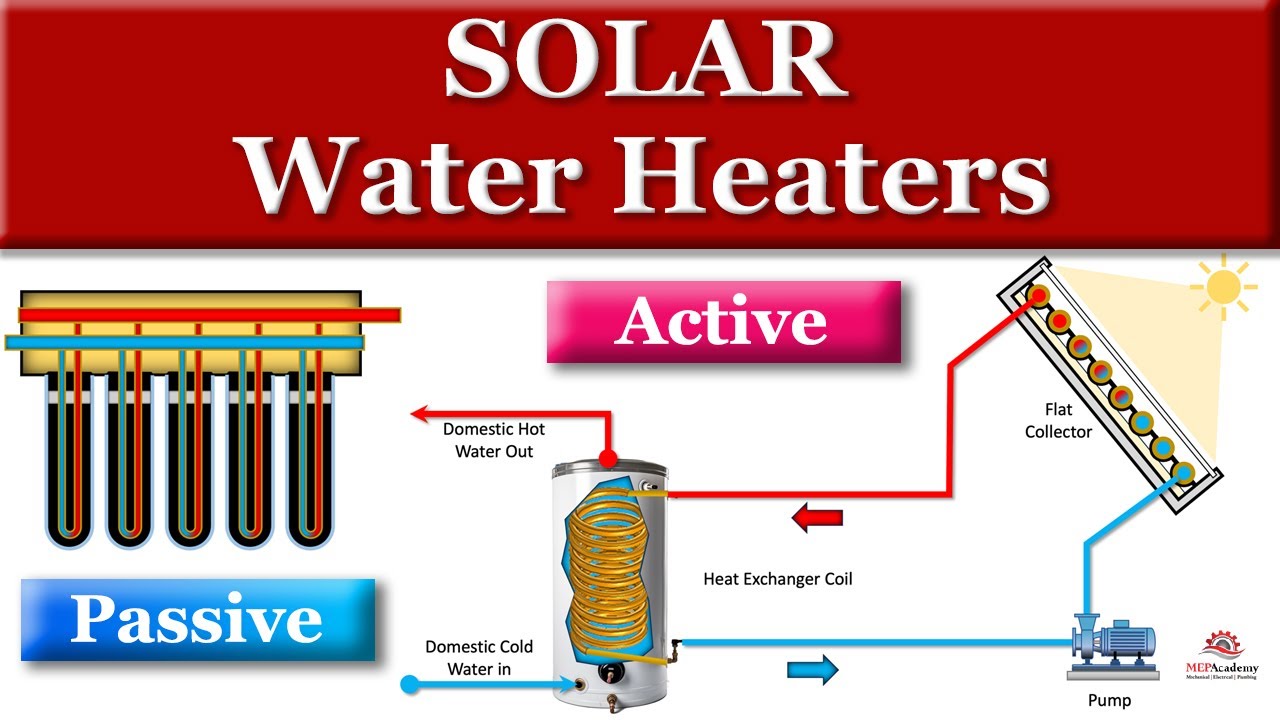
In this video, we'll explain the inner workings of both Active and Passive Solar Water Heaters, examining their advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications. Active Solar Water Heaters are a marvel of engineering that relies on fluid circulation, advanced controls, and the tireless power of pumps to efficiently warm water for diverse applications in commercial and residential buildings. On the flip side, the Passive Solar Water Heater takes a more elegant, simplified approach, using nature's thermosyphon principle to create a self-sustaining flow of warm water. Solar water heaters are described by the type of solar collector and circulation system that they use. Active Solar Water Heaters Active solar water heaters come in two main types: direct circulation systems and indirect circulation systems. These systems harness solar energy to heat water for various applications, such as domestic hot water, space heating, or industrial processes. Let's delve into the specifics of each type: Direct Circulation Systems Direct circulation systems, also known as open-loop systems, involve the direct transfer of water from the collector to the end-use application without an intermediate heat transfer fluid. This simplicity makes them suitable for regions with mild climates where freezing is not a concern. Indirect Circulation Systems: Indirect circulation systems, also known as closed-loop systems, use an intermediate heat transfer fluid to transfer thermal energy from the solar collectors to the water in the storage tank. This allows them to operate in colder climates without the risk of freezing. Passive Solar Water Heater A Passive Solar Water Heater operates without the need for mechanical pumps or electrical components. These systems are less expensive than Active systems but are usually not as efficient. Without the need for moving parts, these systems can be more reliable and last longer. Thermosyphon Systems Like an active system, a passive system relies on a solar collector to absorb sunlight. This collector is often a dark-colored, heat-absorbing material like metal or special coatings on a surface. In a passive system, the sunlight heats the water directly without the use of a separate fluid. The collector absorbs the solar energy, and this heat is transferred directly to the water circulating through or stored in the system. Thermosyphon Principle The core principle behind passive solar water heaters is thermosiphon. As water absorbs heat, it becomes lighter and rises. Simultaneously, colder, denser water descends to replace it. This creates a natural circulation of water through the system. The heated water typically rises from the collector to a storage tank located at a higher elevation. This tank is positioned above the collector to facilitate the thermosiphon effect. The warm water is stored in this tank until it is needed. When hot water is required, it is drawn from the storage tank. The cold water that enters the collector to replace it completes the natural circulation loop, creating a continuous flow of warm water if there is sunlight. Passive solar water heaters are characterized by their simplicity and reliance on natural processes. They are often used in residential and small-scale applications, providing a cost-effective and energy-efficient way to obtain hot water. While they may not be as suitable for large-scale commercial projects, the principles of passive solar design can still be applied to aspects of building construction to enhance energy efficiency and reduce reliance on traditional heating systems. Storage Tanks and Solar Collectors Most solar water heaters require a properly insulated storage tank. These tanks typically feature an extra outlet and inlet that are linked to the collector. In two-tank configurations, the solar water heater heats the water in advance of it entering the standard water heater. Conversely, in one-tank setups, the backup heater is integrated with the solar storage within a single tank. Collector Types Solar water heaters for residential properties usually use three different types of collectors to capture sunlight and convert it into heat for heating water. These collectors are critical components that determine the efficiency and performance of the system. Here are the main types of collectors used in solar water heaters: Flat-Plate Collectors Flat-plate collectors are the most common type and consist of a flat, insulated box with a transparent cover (usually glass) on top. Inside the box is a dark absorber plate, typically made of metal or other materials with high thermal conductivity. Sunlight passes through the transparent cover and strikes the absorber plate, which absorbs the solar energy and converts it into heat. The heat is then transferred to a fluid (usually water or a heat transfer fluid) flowing through tubes attached to the absorber plate. Flat-plate collectors are versatile and used in both residential and commercial solar water heating systems. They are suitable for moderate climates and are effective for domestic hot water applications. Evacuated Tube Collectors Evacuated tube collectors consist of rows of glass tubes with an outer and inner tube. The air is evacuated from the space between the tubes to create a vacuum, reducing heat loss through conduction and convection. Like flat-plate collectors, sunlight passes through the outer glass tube and strikes an absorber within the inner tube. The absorber transfers the heat to a fluid circulating within the tube. Evacuated tube collectors are more efficient than flat-plate collectors, especially in colder climates. The vacuum insulation minimizes heat loss, allowing them to capture solar energy even on cloudy days. Evacuated tube collectors are commonly used in colder climates and are suitable for both residential and commercial applications. Integral Collector Storage (ICS) Systems (Passive System) ICS systems, also known as batch or breadbox collectors, integrate the solar collector and the storage tank into one unit. The collector is a black tank with a transparent cover, or dark tubes in an insulated tank. Water is heated directly in the collector, eliminating the need for separate pipes or heat exchangers. The heated water is stored in the same unit until it is used. ICS systems are simple and cost-effective, often used in residential settings for domestic hot water applications. There should be a tempering valve that allows cold water to be mixed with the hot water coming from the tank. They are used in open loop systems and aren’t suitable for cold climates. The choice of collector depends on factors such as climate, available space, and the specific requirements of the solar water heating system. Each type of collector has its advantages and disadvantages, and the selection is often tailored to meet the needs of the project. ...



Geyser Repair in Ghaziabad Are you looking for geyser repair service in Ghaziabad at low cost? We offer geyser repair in Ghaziabad with quick and efficient solutions for geyser issues like no heating, leaks, or thermostat faults. Geyer expert technicians offer doorstep service, precise diagnosis, and reliable repairs for all brands. Visit: Microwave Oven Repair in Ghaziabad
ResponderEliminarRefrigerator Repair in Ghaziabad
Refrigerator Gas Refilling in Ghaziabad
Washing Machine Repair in Ghaziabad